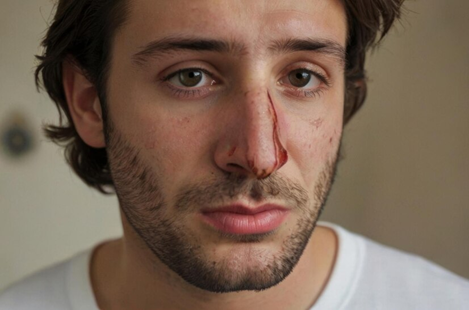
A broken nose, also known as a nasal fracture, is a common injury that occurs when there is a break or crack in the bone or cartilage of the nose, typically from a sudden impact. This type of injury can result from various activities, such as contact sports, falls, or accidents.
Symptoms of a Broken Nose
Pain and Swelling: Pain in or around the nose is typical, along with swelling that may cause the nose to appear crooked or misshapen.
Bruising: Bruising around the nose and eyes (often referred to as “black eyes”) may develop.
Nasal Bleeding: You might experience bleeding from the nose or a blocked sensation, making it hard to breathe through one or both nostrils.
Crackling Sensation: A crunching or crackling sound may occur when touching the nose.
If you notice any of the following severe symptoms, seek immediate medical attention:
- Heavy bleeding that doesn’t stop
- Clear fluid draining from the nose
- Difficulty breathing
- Severe headache, double vision, or blurred vision
At-Home Care for a Broken Nose
For minor fractures, self-care measures can help manage symptoms:
Ice Therapy: Apply an ice pack wrapped in a towel to your nose for 15-20 minutes, several times a day, to reduce swelling.
Pain Relief: Over-the-counter medications can alleviate pain.
Nosebleed Management: If bleeding occurs, sit upright, lean forward, and pinch your nose above the nostrils for 15 minutes.
Rest: Elevate your head while sleeping to decrease swelling.
When to Seek Medical Attention?
Consult a doctor if:
- Your nose appears crooked or misshapen
- Swelling persists beyond three days
- Breathing difficulties continue despite treatment
- Pain remains severe despite medication
Your doctor will conduct a physical examination and may recommend imaging tests, like X-rays, to assess the extent of the injury.
Treatment Options
Treatment depends on the severity of the injury:
Minor Fractures: Often, no specific treatment is necessary. Follow at-home care guidelines.
Severe Fractures: A doctor may perform a closed reduction (manually realigning the nose), and in cases of significant displacement or injury to the septum, surgical options such as rhinoplasty or septorhinoplasty may be needed.
Prevention Strategies
To reduce the risk of a broken nose:
Wear Protective Gear: Use helmets and face guards during sports.
Practice Safety: Ensure proper footwear to prevent falls and always wear seatbelts in vehicles.
Exercise Caution: Be mindful in environments where accidents are likely.
Most broken noses heal within three weeks without complications. However, if you are concerned about the appearance or functionality of your nose post-injury, reconstructive surgery may be an option. Always consult your doctor for appropriate assessment and treatment options.